A Secretive US Space Plane Will Soon Test Quantum Navigation Technology
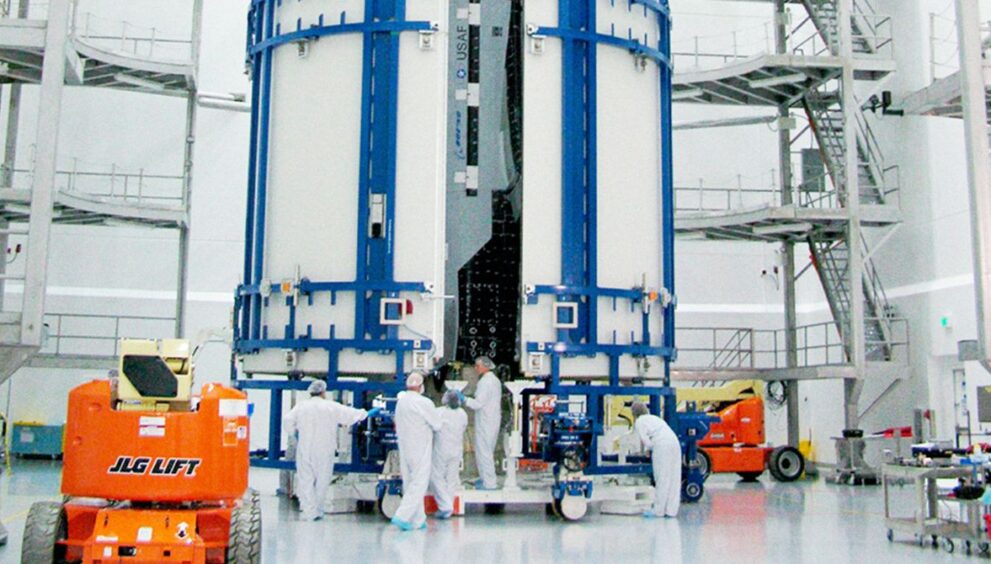

The X-37B, the US Space Force’s secretive space plane, will soon take flight again.
On Monday, the Space Force announced that it will fly the small, Space Shuttle–shaped vehicle on the program’s eighth mission next month. The launch of the vehicle, on a Falcon 9 rocket, is scheduled to occur no earlier than August 21 from Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
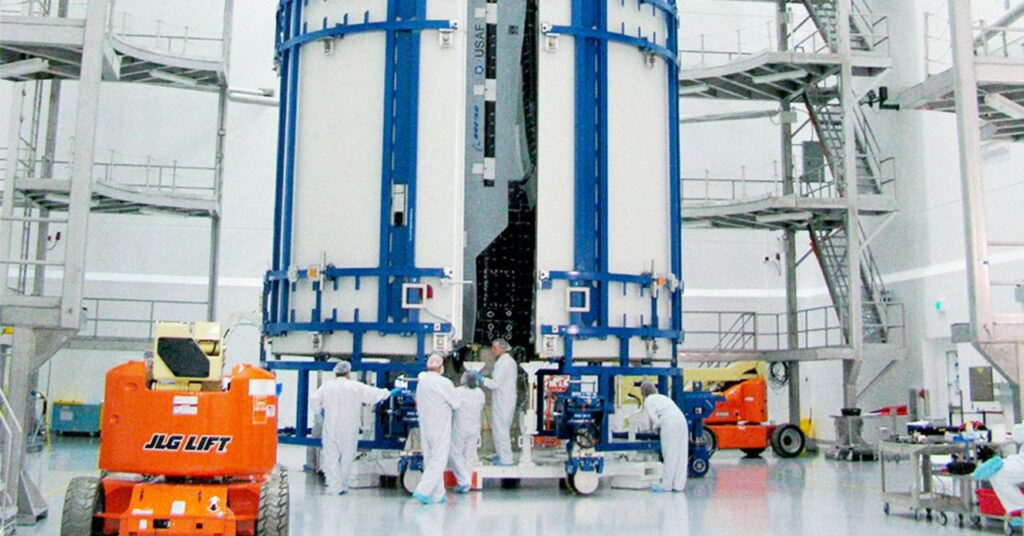
There are two active X-37Bs in the Space Force fleet, both built by Boeing. The first made its debut flight in April 2010. Since then, the two uncrewed spacecraft have made a succession of longer flights. The first made its longest and latest flight from 2020 to 2022 over a span of 908 days. The second flew more recently, landing at Vandenberg Space Force Base on March 7 after 434 days in orbit.
It’s likely that the first of these two vehicles, both of which are about 29 feet (9 meters) long and roughly one-quarter the length of one of NASA’s Space Shuttle orbiters, will launch next month.
Some Details About the Upcoming Flight
Over the past decade and a half, the Space Force has largely remained silent about the purpose of this space plane, flying classified payloads and providing only limited information about the purpose of each flight.
However, for this flight, OTV-8, the military has provided a bit more detail about its intentions. The vehicle will fly with a service module that will expand its capacity for experiments, allowing the space plane to host payload for the Air Force Research Laboratory and the Defense Innovation Unit.
The mission’s goals include tests of “high-bandwidth inter-satellite laser communications technologies.”
“OTV-8’s laser communications demonstration will mark an important step in the US Space Force’s ability to leverage commercial space networks as part of proliferated, diversified, and redundant space architectures,” said General Chance Saltzman, US Space Force chief of space operations, in a statement. “In so doing, it will strengthen the resilience, reliability, adaptability, and data transport speeds of our satellite communications architectures.”
Navigating in a World Without GPS
The space plane will also advance the development of a new navigation technology based on electromagnetic wave interference. The Space Force news release characterizes this as the “highest-performing quantum inertial sensor ever tested in space.”
Boeing has previously tested a quantum inertial measurement unit, which detects rotation and acceleration using atom interferometry, on conventional aircraft. Now, an advanced version of the technology is being taken to space to demonstrate its viability. The goal of the in-space test is to demonstrate precise positioning, navigation, and timing in an environment where GPS services are not available.
“Bottom line: Testing this tech will be helpful for navigation in contested environments where GPS may be degraded or denied,” Saltzman said in a social media post Monday, describing the flight.
Quantum inertial sensors could also be used near the moon, where there is no comparable GPS capability, or for exploration further into the solar system.
Notably, the small X-37B is back to launching on a medium-lift rocket with this new mission. During its most recent flight that ended in March, the space plane launched on a Falcon Heavy rocket for the first time. This allowed the X-37B to fly beyond low Earth orbit and reach an elliptical high Earth orbit.
This story originally appeared on Ars Technica.